|
|
|
|
Economy
North Sumatera is famous for its plantations and oil resources. Medan was once called the "Paris of Sumatera" refelcting its many rich foreign oil and rubber barons and their glamorous life style in its height. Today there are vast plantations along all the east coast and in certain areas in the west. Tha main cash crops are rubber, tea, palm oil, cocoa, coffee and tobacco. The capital North Sumatera is Medan, which is also a kind of informal capital for all of Sumatera. 305 of Indonesia's export goes through Medan.
|
| The Plantation Industry |
In 1863 the first tobacco plantation was established in Deli (Medan). It became a success and was followed by many other plantations. The Deli tobacco reached fame for its quality, especially as a cigar wrapper. A typical tobacco plantation covered 700-900 hectares and employed 500-800 coolies. Today a typical plantation work so Chinese and Javanese were contracted for three years at a time. The wages were low and the workers had to endure many deseases and other handships. All Dutch plantations were nationalized during the conflict with the Netherlands over New Guinea. Most tobacco and tea plantations have since been turned into oil palm and rubber plantations. two sub-regencies of Medan still bear names given by foreign plantation owners. Helvetia was the name of a plantation owned by a Swiss citizen. Polonia was the huge plantation of the Polish Baron Michalsky.
The oil palm or Kelapa sawit (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) can grow between 12 degrees north and 12 degrees south of the equator and between 0 and 500 meter above sea level. The palm oil industry of Indonesia started in 1911 and is today the second biggest in the world after Malaysia.Palm oil is also produced in Thailand, Africa and South America. the so-called:"Sumatera Oil Palm Belt" is almost the whole of Sumatera's east coast from Lhokseumawe in Aceh to Lampung in the far south. Certain areas of the west coast of Sumatera such as Meulaboh, Singkil, Pasaman and Bengkulu are also suitable areas. The first harvest after a tree has been planted takes place after 30 months. The fruit cluster weighs then about 3-5 kg. Mainly big state and private companies own the plantations. Small farmers own a small part though. The oil is used for cooking oil, margarine and shortening, ice cream, soap, shampoo, detergents, plastics and in teh leather and textile industries.
The first to produce tobacco in North Sumatera were Melayu and KAro farmers who even exported the produce to Penang. In 1882 teh English Governor in Penang sent an investigator to the east coast of Sumatera. In the 1860'ies Jacobus Nienhuys, on behalf of Pieter van der aren & Consortium, came to Deli and tried to buy from local farmers through advance payments. This failed and instead he started his own plantation and land given by the Sultan. In 1864 the first shipment was sent to Rotterdam and received very positively. Production increased, as the prices were extremely good. Other plantations, were established, for example Deli Maatschapij, Deli Batavia Maatschapij, Tabak Mij Arendsburg and many more. In 1889 there were 170 tobacco plantations in Deli Serdang, Langkat and Siak. It was however found out that the best area was restricted to the land between the rivers sei Wampu and Sei Ular. In 1957 all plantations were taken over by two companies, Vereinigde Deli Maatschapij and Senebah Maatschapij, a total of 59,000 hectares. The Deli tobacco is today still of high quality and sell at a high price, however the productivity is low. |
|
|
|
|
|
| Five Uruguayan surfers hoping to catch some waves off Indonesia's Indian Ocean Mentawai islands got more than ...more>> |
|
 |
The Choice Hotels ...!! |
|
|
 |
Exchange Rate for IDR |
|
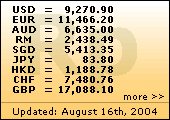 |
 |
Events Calendar |
|
 |
| |
| |
|